Fetal abnormalities » Placenta, umbilical cord
Morbid adherent placenta
Prevalence:
- 1 in 400 pregnancies.
- Placenta previa with history of previous cesarean section (CS): 3% for 1 CS, 10% for 2 CS, >50% for ≥3 CS.
- A morbidly adherent placenta includes placenta accreta (chorionic villi attach to myometrium), increta (chorionic villi invade into the myometrium) and percreta (chorionic villi invade through the myometrium).
Ultrasound diagnosis:
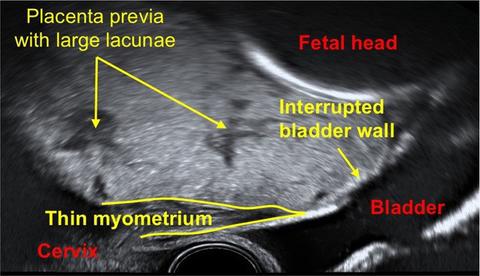
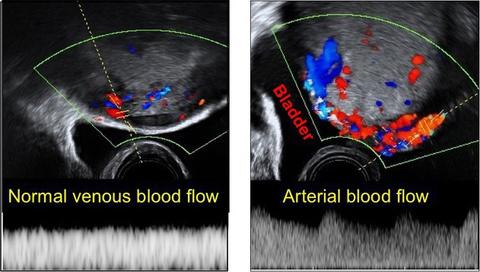
- Multiple vascular lacunae (spaces) within the placenta (‘Swiss cheese’ appearance) with turbulent flow (peak systolic velocity >15 cm/s),
- Retroplacental myometrial thickness of <1 mm.
- Loss of normal retroplacental hypoechogenic zone.
- Blood vessels and placental tissue bridging uterine-placental margin, myometrial-bladder interface, or crossing uterine serosa. Exophytic masses invading the urinary bladder.
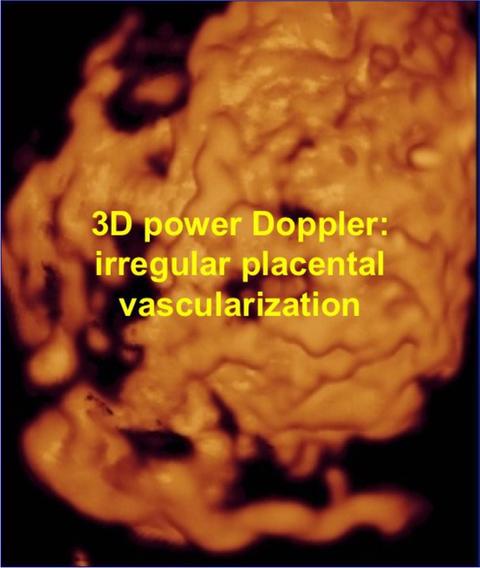
- Irregular vascularization involving the whole uterine serosa–bladder junction, visualised with 3-dimensional power Doppler.
Investigations:
- MRI is recommended if ultrasound findings are inconclusive.
- Fetal antenatal surveillance should be standard.
Follow up:
- Follow-up should be standard.
Delivery:
- Place: hospital with expertise in the management of this condition and a blood bank that can facilitate transfusion of large amounts of various blood products. There is a high chance of hysterectomy and major hemorrhage.
- Time: 36 to 37 weeks.
- Method: cesarean section.
Prognosis:
- Maternal mortality 5-10%, morbidity 75%.
- Early diagnosis reduces mortality and morbidity by 50%.